Adaptive Introgression 2025
Identification of the Novel Stripe Rust Resistance Gene YrSA in Wheat Cultivar Samara
Stripe rust, a devastating wheat disease worldwide, is caused by the obligate biotrophic fungus Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst). Pst’s ability to produce a large amount of urediniospores that can be dispersed over long distances via wind in a short period of time enables it to cause serious disease epidemics. Stripe rust has been reported in more than 60 countries across all continents where wheat is grown. Serious stripe rust epidemics have been frequently observed globally, adversely affecting grain filling and leading to low grain yield, poor quality and/or big spending on the use of chemicals to control the disease. In the United States, stripe rust epidemics have historically occurred in the states west of the Rocky Mountains. However, its geographical footprint has significantly expanded due to the emergence of more aggressive Pst races that are better adapted to warmer conditions and have had broader virulence profiles since 2000, resulting in frequent epidemics (occurring every two to three years) with severe yield losses. More stripe rust resistance genes are urgently needed to facilitate breeding durable stripe rust-resistant cultivars.
The Oklahoma State University Wheat Improvement Team identified a new stripe rust resistance gene, designated YrSA, in wheat cultivar Samara. YrSA confers resistance to PSTv-37 (Figure 1), the predominant Pst race with a frequency of over 62% in the U.S. in 2024. Thus, YrSA can be widely used to enhance wheat stripe rust resistance in the U.S. YrSA was delimited to an interval of 1.65 Mb between 784.71 Mb and 786.36 Mb on chromosome arm 2AL in an F2:3 population from the cross Samara × Jagalene, and the mapping result was further confirmed in a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population from the same cross(Figure 2). YrSA is a new stripe rust resistance gene different from other genes previously reported on chromosome arm 2AL based on their locations, origins and responses to Pst races. The physical order of YrSA with other permanently named Yr genes on 2AL is Yr1-Yr86-Yr32-YrSA. YrSA also confers resistance to other U.S. representative Pst races PSTv-14 (IT = 4), PSTv-40 (IT =2) and PSTv-52 (IT =2). Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) markers flanking YrSA, such as Stars-KASp1837 and Stars-KASP1951, can be used to tag YrSA in cultivar development (Figure 3).

Figure 1. Typical responses of Samara (1), Jagalene (2) and F3 plants (3-7) to Pst race PSTv-37 in the F2:3 population from the cross Samara × Jagalene.
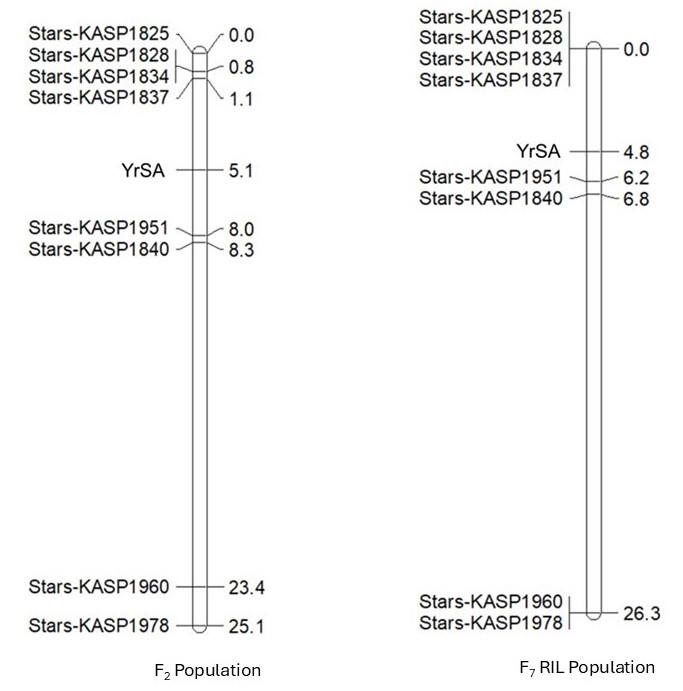
Figure 2. Linkage maps showing genomic location of YrSA in the F2 population (left) and F7 RIL population from the cross Samara × Jagalene. Molecular markers and genetic distance in centimorgan (cM) are on the left and right sides of the linkage maps, respectively.
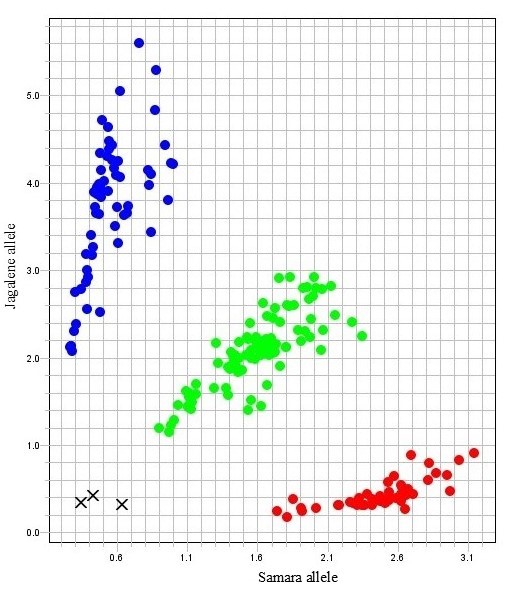
Figure 3. An allelic discrimination plot showing segregation of the Samara (red), Jagalene (blue) and heterozygous (green) alleles at Stars-KASP1837 in an F2 population from the cross Samara ×Jagalene. X represents the negative control (water).
Discovery of a Novel QTL for Stripe Rust Resistance
Landraces, which were selected for biotic and abiotic stress resistance by nature and farmers under suboptimal agricultural systems, have been proven to be a rich source of genetic variability. The Fertile Crescent has been the original home to wild wheat and landraces, and new adaptive traits suitable for new environments were selected during the process of domestication and the spread of domesticated wheat. Many disease and pest resistance genes have been identified in landraces from the Fertile Crescent region. PI 622129 is a landrace from the Fertile Crescent region and exhibits high resistance to predominant Pst races in the U.S. (Table 1).
| Wheat | PSTv-4 20WA-19-2 | PSTv-14 15-306 | PSTv-37 21OK-03 | PSTv-40 22WA-43 | PSTv-52 14-194-sp3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stardust | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| PI 622129 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| AvS (CK) | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
a PSTv-4: virulent to Yr1, Yr6, Yr9, Yr17, Yr27, YrSP, and Yr76; PSTv-14: virulent to Yr1, Yr6, Yr7, Yr8, Yr9, Yr17, Yr27, Yr43, Yr44, Yr85 (=YrTr1), YrExp2, and Yr76. PSTv-40: virulent to Yr6, Yr7, Yr8, Yr9,Yr10, Yr24, Yr27, Yr32, Yr43, Yr44, Yr85 (=YrTr1),and YrExp2; and PSTv-52: virulent to Yr6, Yr7, Yr8, Yr9, Yr17, Yr27, Yr43, Yr44, and YrExp2 (Wang et al. 2022).
The Wheat Improvement Team genotyped an RIL population from PI 622129 × Stardustusing single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) generated by genotyping-by-sequencing. The RIL population was evaluated for responses tothe Pst race PSTv-37 at the seedling stage in three environments, andquantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis revealedfour QTL for stripe rust resistance on chromosome arms 2DS, 5BS, 2AL and 7BL (Figure 4). Of these, QYr.stars-2DS and QYr.stars-5BS are major QTL explaining 21-38% and 11.6-27.2% of the total phenotypic variance, respectively (Table 2), in three experiments. QYr.stars-2DS is a new stripe rust resistance locus that was identified in the interval of 2.58-5.54 Mb on chromosome arm 2DS based on the Chinese Spring IWGSC RefSeq v2.1 reference genome.Another QTL, QYr.stars-5BS, was close to Yr47 and was delimited to the interval 8.1–9.0 Mb in the reference genome. QYr.stars-2AL and QYr.stars-7BL were mapped to the terminal and QTL-rich regions on chromosome arms 2AL (750.8–752.5 Mb) and 7BL (718.1–721.2 Mb), respectively. KASP markers were developed to facilitate the rapid introgression of these QTL into locally adapted lines via marker-assisted selection.
Figures 4a-d. Partial linkage maps showing locations of stripe rust resistance QTL identified in PI 622129. Blue, red and green represent 2024 experimental trials in Stillwater, 2025 trials in Stillwater and the 2024 Pullman experiments, respectively. Genotyping by sequencing single nucleotide polymorphism (GBS-SNP) markers – represented by the genomic locations in the Chinese Spring International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC) RefSeq v2.1 reference sequence – are shown on the right and genetic distances on the left of the linkage maps. The vertical dot lines mark the threshold logarithm of the odds (LOD) value of 2.5, and the confidence locations of quantitative trait loci are highlighted in red bars on the maps.
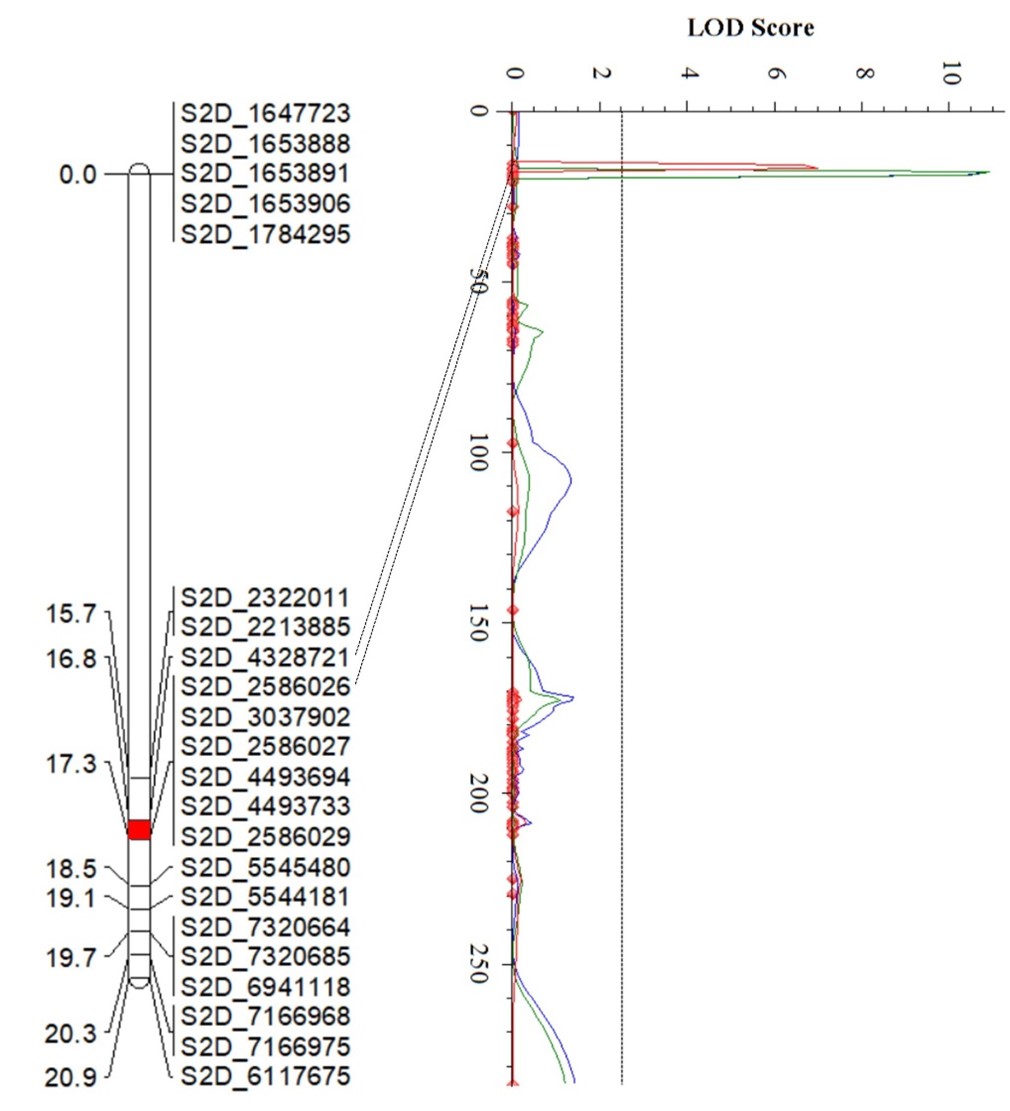
Figure 4a.QYr.Stras-2DS
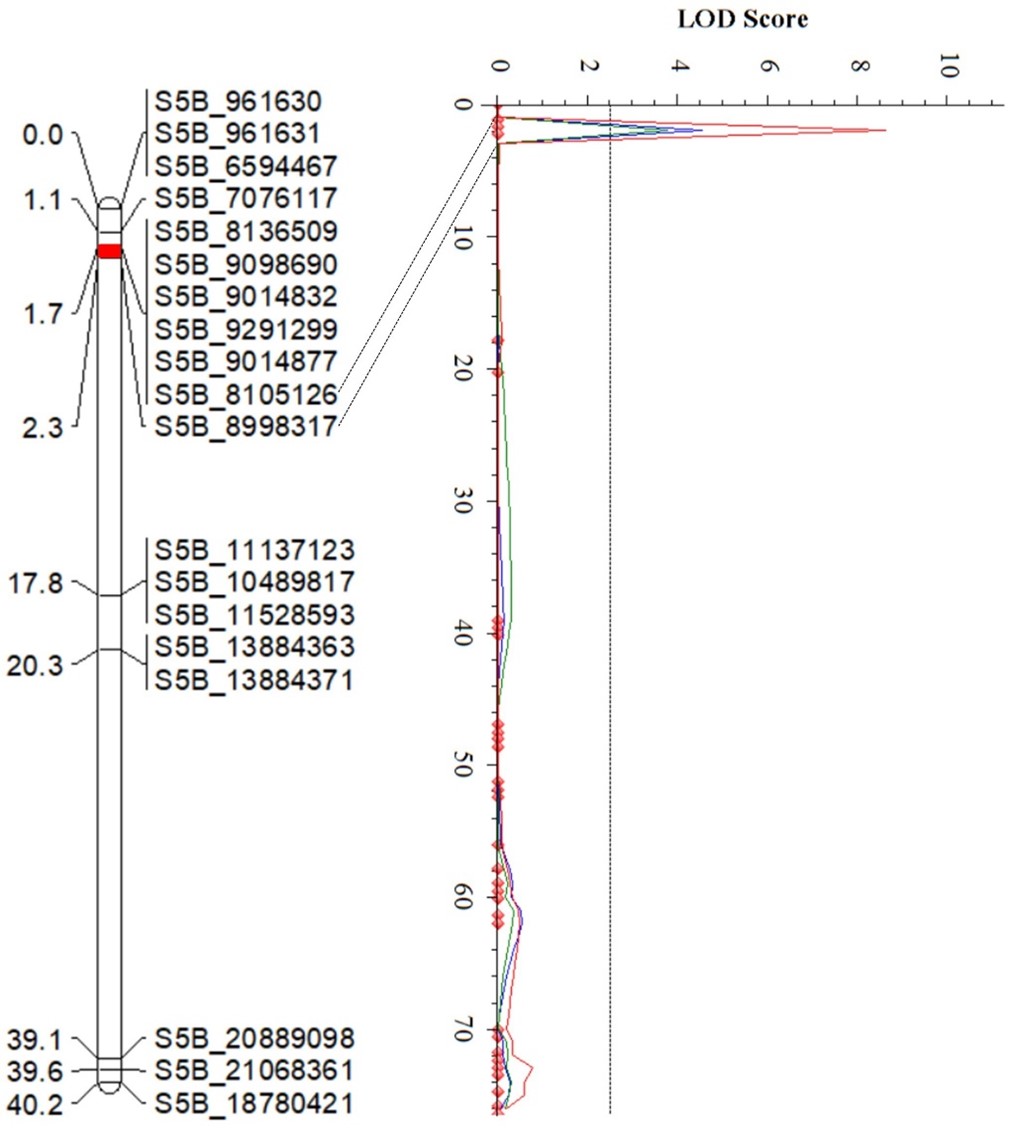
Figure 4b.QYr.Stars-5BS
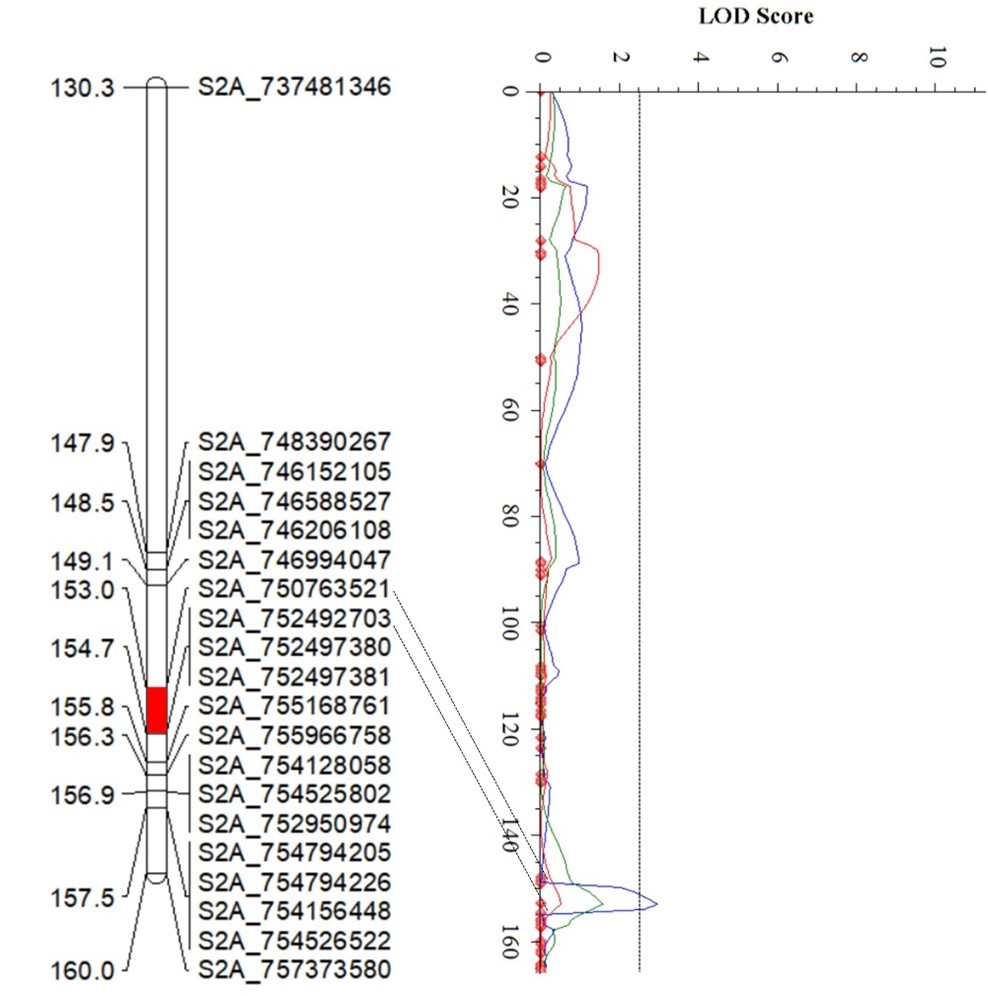
Figure 4c.QYr.Stars-2AL
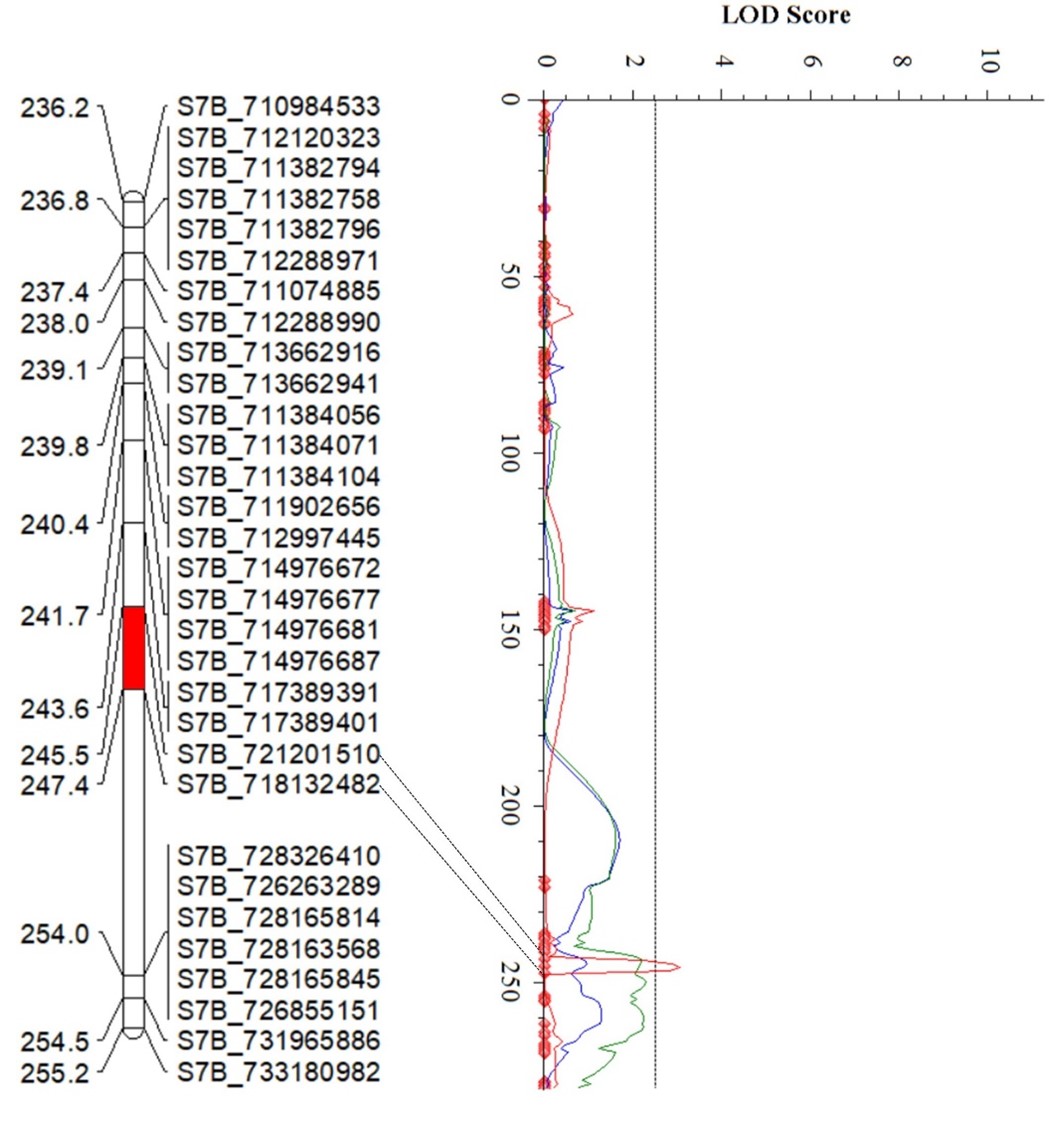
Figure 4d.QYr.Stars-7BL
Tables 2a-c. Flanking markers, logarithm of the odds (LOD) values, R2 values and additive effects of four QTL for stripe rust resistance identified in PI 622129.
| QTL | Left marker | Right marker | LOD | R2 (%) | Additive effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QYr.stars-2AL | S2A_750763521 | S2A_752492703 | 3.0 | 8.0 | -0.60 |
| QYr.stras-2DS | S2D_2586029 | S2D_5545480 | 10.9 | 34.9 | -1.24 |
| QYr.stars-5BS | S5B_8105126 | S5B_8998317 | 4.5 | 13.0 | -0.75 |
| QTL | Left marker | Right marker | LOD | R2 (%) | Additive effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QYr.stras-2DS | S2D_2586026 | S2D_4328721 | 7.0 | 21.0 | -1.02 |
| QYr.stars-5BS | S5B_8105126 | S5B_8998317 | 8.6 | 27.2 | -1.16 |
| QYr.stars-7BL | S7B_718132482 | S7B_721201510 | 3.1 | 8.4 | -0.66 |
| QTL | Left marker | Right marker | LOD | R2 (%) | Additive effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QYr.stras-2DS | S2D_2586029 | S2D_5545480 | 10.9 | 38.0 | -1.41 |
| QYr.stars-5BS | S5B_8105126 | S5B_8998317 | 3.8 | 11.6 | -0.77 |
Improved Germplasm with High Resistance to Leaf Rust and Stripe Rust
Wheat landraces PI 622129, PI 62066 and PI 622111 are highly resistant to both leaf rust and stripe rust. The Wheat Improvement Team developed a RIL population from the cross PI 622129 × Stardust, and a set of 37 F8 RILs with better agronomic traits than PI 622129 and high resistance to both leaf rust and stripe rust were selected. These RILs carry a leaf rust all-stage resistance gene, designated Lr622066, on chromosome 5BS and multiple QTL for stripe rust resistance. Seeds are currently being increased for field tests.
A set of 38 RILs resistant to both leaf rust and stripe rust was also selected from the cross PI 622066 × TAM 110. Both PI 622066 and TAM 110 are highly resistant to leaf rust, whereas PI 622066 is highly resistant to stripe rust. WIT is currently characterizing the leaf rust and stripe rust resistance genes in the two parents, and the selected RILs can be directly used in cultivar development.
Another set of 69 F8 RILs from PI 622111 × Yuanyu 3 was also selected. Both PI 622111 and Yuanyu 3 are highly resistant to stripe rust, and these RILs had near-immune resistance to Pst race PSTv-37. Given that PI 622111 carries the leaf rust resistance gene Lr622111, we expect that some of these RILs are resistant to leaf rust. Thus, we currently evaluate these lines for leaf rust resistance in greenhouses and genotype them using KASP markers flanking Lr622111. The RILs that also carry Lr622111 will be evaluated in fields in 2026.
In addition, a large set of backcross progenies is being tested for the presence or absence of a set of biotic stress resistance genes/QTL, including Lr81, Lr622111, Qlr.stars-1RS, QLr-Stars-2DS and QLr-Stars-6BL, Pm59, Pm63, Pm65, Pm351817, Gb8 and Gb9. Those carrying the target genes will be tested in fields in 2026.
Acknowledgments
Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the USDA. The USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
